
Your Analysis Assistant
Vision Data Acquisition Software
Vision is a revolutionary software package that provides exceptional freedom to design, conduct, and review all procedures associated with any material experiment.
The Vision test environment will collect all data acquired in a test sequence and organize it in archived data structures along with the test sequence definitions and data analysis tools.
The experiment can always be recalled or reproduced. Data and test conditions can be shared over the Internet to allow collaborative research.
Vision has Four Interconnected Units
Measurement tasks pass data to the plotting and analysis tasks in the Test Definition during execution.
Program control tasks manage external instruments, control the order of task execution, and adjust test parameters during execution of a Test Definition.
Radiant’s Non-linear Materials Testers running under the Vision Materials RDP Operating System reduces Cost of Test by a factor greater than 10 over any other ferroelectric tester.
The Power of Vision
Test Definitions and Data Sets
Radiant’s Precision Line of Test Systems are driven by Vision Software. Vision Software is a framework that loads a variable series of independent agents known as Tasks. Tasks are configurable objects that perform the procedures of an experiment and collect and analyze any measured data. Such an experiment is called a Test Definition.
The true power of Vision is in grouping Tasks together into Test Definitions to form custom experiments. The user is not tied to running one specific Task at a time. The Test Definitions may consist of any number of Measurement Tasks. Researchers can create a DataSet to hold any number of arbitrary Test Definitions. A single Test Definition - the Current Test Definition (CTD) - represents an experiment that is ready for immediate execution. On execution, the Test Definition, along with the measured data, are permanently archived to the DataSet as and Executed Test Definitions (ETD). Vision's "Innovative Test Editor" let's researchers create and document complex Test Definitions using type-specific icons to represent Tasks.
All Tasks include a Task Instructions button on their configuration (and data presentation) dialogs. The Task Instruction pages include Task theory, where appropriate, a complete and detailed discussion of every control on the configuration dialog, a detailed discussion of the Task execution and a history of changes to the Task.
New Tasks
Additional data filters and measurement tasks have beenadded to the VISION library, including:
Tasks
Hardware Tasks
These are Tasks that send signals to a tester through the driver and apply a voltage profile to the sample. These also may communicate with other instruments attached to the tester or to the host computer. Hardware Tasks normally apply a voltage pro file to the sample. Testers may apply voltages of up to ±10 Volts, ±100 Volts, ±200 Volts, or ±500.0 Volts depending on tester model. Voltages of up to ±10,000 Volts may be applied with the addition of an accessory High-Voltage Interface (HVI) and High Voltage Amplifi er (HVA).
Hardware Tasks include:
-
Waveform
Applies a sine, square, triangle or user-defined voltage waveform to stress the sample. The waveform is of user-defined voltage, frequency and duration.
-
DC Bias
Applies a constant user-defined voltage to the sample for a user-defined duration.
Measurement Tasks
These are Hardware Tasks that receive data from the tester. Measurement Tasks include, but are not limited to:
-
Hysteresis
This Task measures sample polarization (μC/cm2 ) response to a Task-applied voltage pro file. The pro file is of user-specified maximum voltage and period (ms) (Period = 1000/frequency (Hz)). Pro files are normally standard bipolar (triangular), but may be monopolar, double-bipolar, sinusoidal or user-speci fied.
-
Small Signal Capacitance
This measurement captures the sample's capacitance as a function of voltage. It measures the capacitance at each voltage step using a very small stimulus signal to eliminate polarization -switching components of the sample response.
-
PUND
A standard five-pulse ferroelectric sample characterization measurement that captures both switching (remanent + non-remanent) and non-switching (non-remanent) polarization ( μC/cm2). Pulse width and voltage are under user control.
-
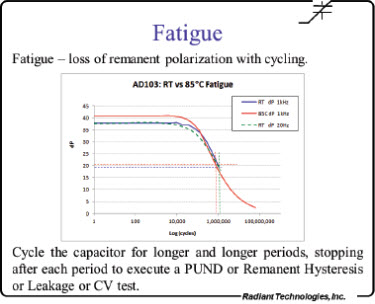
Fatigue
Performs a series of stress/measure sequences. In the stress sequence the sample is submitted to a switching waveform. At the end of the waveform period, a PUND measurement is made to capture the sample’s polarization response. Each subsequent stress period may have its duration increased to better serve a logarithmic analysis.
-
Leakage
Captures the current through a sample induced by a steady-state, DC Bias voltage. Voltage and measurement duration are user-defined.
-
Curve Energy
Determines the energy returned and the energy lost from a charged capacitor. It is useful for measuring power capacitors for new energy generating systems.
-
General Monopolar
The General Monopolar Task allows up to five independently con figured monopolar Hysteresis measurements to be made in sequence in order to execute a PUND measurement using continuous waveforms. Each measurement may be preceded by an unmeasured presetting pulse or poling DC Bias period.
Optional Tasks Include:
-
Piezo-Electric
Captures a sample’s displacement as a function of voltage profile along with the sample’s polarization response. An external displacement measurement instrument must be attached to the tester to make this measurement.
-
Magnetoelectric
Radiant’s new Magnetoelectric Response Task allows the user to measure the magnetoelectric coupling coefficient in multiferroic materials and composite magnetopiezoelectric devices. The test stimulates a sample with a small AC magnetic field while measuring its charge generation.
-
Pyro-Electric
Sets the sample to a series of temperature by performing GPIB control of an external thermal device. At each temperature it captures the sample’s polarization response and/or small-signal capacitance. These are combined to calculate the pyroelectric coefficient.
-
Transistor
Radiant has introduced an I²C digital-to-analog converter product that can be attached to the Precision Premier II or Multiferroic Test System and is controlled from Vision. The addition of this extra voltage source makes it possible for the testers to measure the performance of thin-ferroelectric- film gate transistors (TFFTs and MFSFETs).
-
DLTS
Deep Level Trap Spectroscopy Task allows the user to measure the population of traps filled during a voltage pulse of a non-linear material and measure the decay rate of the trapped population as a function of temperature.
-
PAINT
PAINT was originally designed to capture the mechanical and acoustic vibrations induced in an ink jet chamber by the pulsing of the piezoelectric element to re an ink droplet. In reality, the PAINT Task in Vision can be used to capture the acoustic response of any activity, including SONAR type measurements in a water tank.
Filters
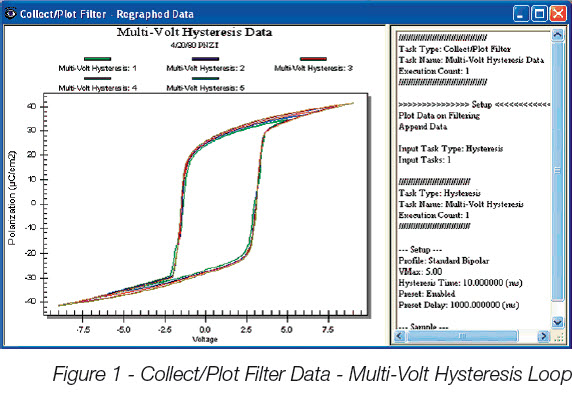
These are Tasks that collect, operate on, store and plot data from one or more Measurement Tasks or other Filters. Filter categories include:
-
Collect/Plot
Simple data collection and plotting.
-
Mathematical Analysis
Combine two measured data vectors into one through addition, subtraction, multiplication or division or perform single vector manipulation on one or more input data vectors. Single vector operations include linear scaling and offset, integration and differentiation.
-
Averaging
Average multiple data vectors together to form a single vector, average one or more single vectors with itself over multiple iterations in a Branch Loop or perform statistical analysis on one or more single vectors. Statistical analysis includes maximum, minimum, mean and standard deviation.
External Sensor Tasks
These are Tasks that import or measure tester SENSOR (1 and/or 2) Port Voltages.
-
SENSOR Collect/Plot Filter
Extract SENSOR 1 port voltages from Input Measurement Task Data if SENSOR 1 capture is enabled.
-
SENSOR 2 Collect/Plot Filter
Extract SENSOR 2 port voltages from Input Measurement Task data if SENSOR 2 capture is enabled.
-
Read SENSOR Task
These Tasks allow the user to directly take a reading of the voltage on SENSOR or SENSOR 2 without having to execute a subsidiary task like Hysteresis.
-
SENSOR Oscilloscope
The oscilloscope task presents a real time display of the voltage on one of the sensor ports of the LCII, Premier, or Multiferroic testers.
External Instrument Control
These are Tasks that communicate with remote instruments through a GBIP bus.
-
LCR Meter
This task allows the user to query an external LCR meter for its measurements including capacitance, loss, and Tan Delta.
-
Set Field
This task allows the user to specify a setting for the superconducting magnet connected to a Quantum Design 6000 controller.
-
Temperature
This Task sets the sample to a series of temperature by performing GPIB control of an external thermal device. At each temperature it captures the sample’s polarization response and/or small-signal capacitance. These are combined to calculate the pyroelectric coefficient.
Program Control
Program Control Tasks are Tasks that control Test Definition sequencing and provide for general Documentation.
-
Branch Tasks
These are Tasks that allow the program to sequence repeatedly over a sequential subset of the Tasks in a Test Definition. Sequencing continues until some condition, that is changing over the Branch iterations, reaches a user-specified threshold.
-
Exit Tasks
These are Tasks that terminate Test Definition execution prematurely based either on comparing an experimental value to a threshold or direct user interaction.
-
If/Then and Endif
This Task pair allows a sequential subset of the Tasks in a Test Definition to be omitted from execution based on the comparison of an experimental value to a threshold.
-
Start Time and Elapsed Time
The Start Time Task establishes a baseline date/time stamp when executed. The Elapsed Time records the elapsed of Task execution relative to the start time date/time stamp.
-
Documentation
Documentation Tasks include the General Information Task that allows extensive text description of the purpose and configuration of the Test Definition, composition of the sample or any other pertinent information. The Hyperlink Task allows links to external files and URLs to be recorded at run-time. Label Tasks allow brief documentation to be recorded by the user at run-time

